What is a gyro sensor?
A gyro sensor is a device that measures angular velocity. Angular velocity is the rate at which an object rotates around a center point. Angular velocity is typically expressed as degrees/second.
What kind of gyro sensors are there?
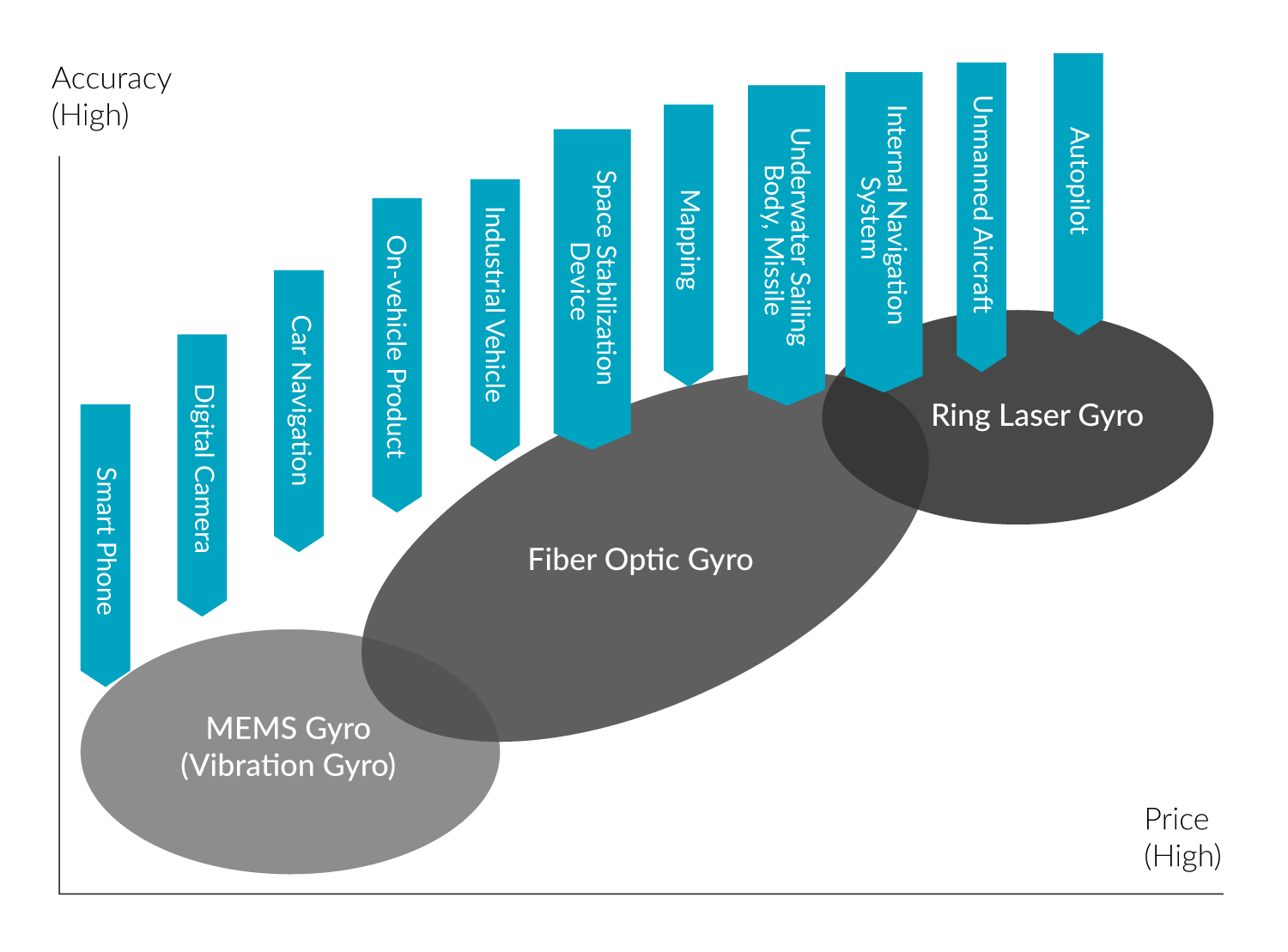
There are many various gyro sensors available on the market. Ring Laser Gyros (RLG) with its high accuracy are suitable for autonomous driving, Unmanned Arial vehicles (UAV) and Inertial Navigations Systems (INS). Fiber Optic Gyros (FOG) are commonly used for missile guidance, spacecraft orientations applications and Inertial Navigation Systems (INS). MEMS gyros on the other hand, with its small format and low cost, are mostly applied in applications where gyro technology previously was too costly such as image stabilization, smartphones, automotive ESC, roll-over prevention and airbag systems as well as various industrial applications such as robotics. Design, accuracy, and cost differ significantly among the different types of gyro sensors, and it is essential to match the right technology with each specific application.
What is a MEMS gyro?
A MEMS gyro is a modern type of gyro sensor that has become popular on the market. The term MEMS stands for Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and is defined as miniaturized electromechanical units (i.e., structures) that are produced using micromachining technologies. This allows for a very compact format and cost-effectiveness.
The operating principle of MEMS gyros is based on a vibrating structure’s tendency to continue vibrating even if its support rotates. This is the Coriolis Effect (or Coriolis Force), and MEMS gyros are often referred to as Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes (CVG). These types of gyro sensors have become more available on the market, and there are many designs principals such as Cylindrical Resonator Gyroscopes (CRG), Piezoelectric Gyroscopes, Turning fork gyroscopes, Wine-glass resonator gyroscopes, and Vibrating wheel gyroscopes. They all make use of the Coriolis Effect.
“The Coriolis Effect is defined as the change of a moving object's trajectory path, which can be observed when the object is observed in a rotating reference system..”
What is a MEMS accelerometer?
An accelerometer is a sensor that emits an electrical signal, which is proportional to the change in speed (acceleration) that the sensor is exposed to. MEMS accelerometer offers the same kind of feedback but with benefits from micromachining techniques, i.e., compact format and cost-effectiveness.
What is an IMU board?
IMU is short for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and simply put it is an electronic device that measures and feedbacks acceleration, angular velocity and sometimes the surrounding magnetic field of a mass. The components allowing for these measurements are accelerometers, gyro sensors, and magnetometers.
The IMU board is equipped with three gyros and three accelerometers to allow for measurements in three dimensions which makes it very suitable for controlling roll, pitch and yaw in car stabilizing applications as well as to feedback movements in the tip of the 6-axis industrial robot manipulator.
What is a MEMS IMU board?
A MEMS IMU board is an IMU board using MEMS gyro sensors and MEMS accelerometer with the benefits that come along with the MEMS technology. These boards are very compact in format and offer communication over RS232, CAN, USB and sometimes Ethernet. They can also be equipped with a built-in GPS receiver.
Principle of MEMS Gyro

What is a gyro sensor?
A gyro sensor is a device that measures angular velocity. Angular velocity is the rate at which an object rotates around a center point. Angular velocity is typically expressed as degrees/second.What kind of gyro sensors are there?
There are many various gyro sensors available on the market. Ring Laser Gyros (RLG) with its high accuracy are suitable for autonomous driving, Unmanned Arial vehicles (UAV) and Inertial Navigations Systems (INS). Fiber Optic Gyros (FOG) are commonly used for missile guidance, spacecraft orientations applications and Inertial Navigation Systems (INS). MEMS gyros on the other hand, with its small format and low cost, are mostly applied in applications where gyro technology previously was too costly such as image stabilization, smartphones, automotive ESC, roll-over prevention and airbag systems as well as various industrial applications such as robotics. Design, accuracy, and cost differ significantly among the different types of gyro sensors, and it is essential to match the right technology with each specific application.

What is a MEMS gyro?
A MEMS gyro is a modern type of gyro sensor that has become popular on the market. The term MEMS stands for Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and is defined as miniaturized electromechanical units (i.e., structures) that are produced using micromachining technologies. This allows for a very compact format and cost-effectiveness.
The operating principle of MEMS gyros is based on a vibrating structure’s tendency to continue vibrating even if its support rotates. This is the Coriolis Effect (or Coriolis Force), and MEMS gyros are often referred to as Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes (CVG). These types of gyro sensors have become more available on the market, and there are many designs principals such as Cylindrical Resonator Gyroscopes (CRG), Piezoelectric Gyroscopes, Turning fork gyroscopes, Wine-glass resonator gyroscopes, and Vibrating wheel gyroscopes. They all make use of the Coriolis Effect.
“The Coriolis Effect is defined as the change of a moving object's trajectory path, which can be observed when the object is observed in a rotating reference system..”
Principle of MEMS Gyro

What is a MEMS accelerometer?
An accelerometer is a sensor that emits an electrical signal, which is proportional to the change in speed (acceleration) that the sensor is exposed to. MEMS accelerometer offers the same kind of feedback but with benefits from micromachining techniques, i.e., compact format and cost-effectiveness.
What is an IMU board?
IMU is short for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and simply put it is an electronic device that measures and feedbacks acceleration, angular velocity and sometimes the surrounding magnetic field of a mass. The components allowing for these measurements are accelerometers, gyro sensors, and magnetometers.
The IMU board is equipped with three gyros and three accelerometers to allow for measurements in three dimensions which makes it very suitable for controlling roll, pitch and yaw in car stabilizing applications as well as to feedback movements in the tip of the 6-axis industrial robot manipulator.
What is a MEMS IMU board?
A MEMS IMU board is an IMU board using MEMS gyro sensors and MEMS accelerometer with the benefits that come along with the MEMS technology. These boards are very compact in format and offer communication over RS232, CAN, USB and sometimes Ethernet. They can also be equipped with a built-in GPS receiver.
What is a gyro sensor?
A gyro sensor is a device that measures angular velocity. Angular velocity is the rate at which an object rotates around a center point. Angular velocity is typically expressed as degrees/second.What kind of gyro sensors are there?
There are many various gyro sensors available on the market. Ring Laser Gyros (RLG) with its high accuracy are suitable for autonomous driving, Unmanned Arial vehicles (UAV) and Inertial Navigations Systems (INS). Fiber Optic Gyros (FOG) are commonly used for missile guidance, spacecraft orientations applications and Inertial Navigation Systems (INS). MEMS gyros on the other hand, with its small format and low cost, are mostly applied in applications where gyro technology previously was too costly such as image stabilization, smartphones, automotive ESC, roll-over prevention and airbag systems as well as various industrial applications such as robotics. Design, accuracy, and cost differ significantly among the different types of gyro sensors, and it is essential to match the right technology with each specific application.

What is a MEMS gyro?
A MEMS gyro is a modern type of gyro sensor that has become popular on the market. The term MEMS stands for Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and is defined as miniaturized electromechanical units (i.e., structures) that are produced using micromachining technologies. This allows for a very compact format and cost-effectiveness.The operating principle of MEMS gyros is based on a vibrating structure’s tendency to continue vibrating even if its support rotates. This is the Coriolis Effect (or Coriolis Force), and MEMS gyros are often referred to as Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes (CVG). These types of gyro sensors have become more available on the market, and there are many designs principals such as Cylindrical Resonator Gyroscopes (CRG), Piezoelectric Gyroscopes, Turning fork gyroscopes, Wine-glass resonator gyroscopes, and Vibrating wheel gyroscopes. They all make use of the Coriolis Effect.
“The Coriolis Effect is defined as the change of a moving object's trajectory path, which can be observed when the object is observed in a rotating reference system..”
Principle of MEMS Gyro

What is a MEMS accelerometer?
An accelerometer is a sensor that emits an electrical signal, which is proportional to the change in speed (acceleration) that the sensor is exposed to. MEMS accelerometer offers the same kind of feedback but with benefits from micromachining techniques, i.e., compact format and cost-effectiveness.
What is an IMU board?
IMU is short for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and simply put it is an electronic device that measures and feedbacks acceleration, angular velocity and sometimes the surrounding magnetic field of a mass. The components allowing for these measurements are accelerometers, gyro sensors, and magnetometers.
The IMU board is equipped with three gyros and three accelerometers to allow for measurements in three dimensions which makes it very suitable for controlling roll, pitch and yaw in car stabilizing applications as well as to feedback movements in the tip of the 6-axis industrial robot manipulator.
What is a MEMS IMU board?
A MEMS IMU board is an IMU board using MEMS gyro sensors and MEMS accelerometer with the benefits that come along with the MEMS technology. These boards are very compact in format and offer communication over RS232, CAN, USB and sometimes Ethernet. They can also be equipped with a built-in GPS receiver.
